Mike Burns Dev Blog
Edu-tech, machine learning, video games, and more! The ongoing projects of Michael Benjamin Burns.
GitHub |
LinkedIn |
Resume |
Game Portfolio Site
Sunday, November 29, 2020
Simultaneous Localization and Mapping (SLAM) Mining Agent
Sunday, October 4, 2020
Particle Filter to Determine 3D Position from Noisy Height Sensors
The agent builds a collection of particles with randomized parameters based on sensor noise and environment variables. It then weights the viability of each particle using a probability density function with the absolute height and radar to ground height. It resamples from the particle pool with replacement based on the weights, propagates them forward in time according to the agent's movement model, and randomizes some of the variables further.
Once the particles have converged to a point that the standard deviation between their locations is low enough, the agent uses a weighted average of the particles to estimate its position. With this position, the agent calculates the turning angle to get to the goal point.
The code for the mars rover and rendering was provided by GaTech; the code for the particle filter and ship's navigation strategy was written by me.
 |
| Add caption |
Tuesday, September 15, 2020
Kalman Filter to Navigate Obstacles Based on Noisy Senor Data
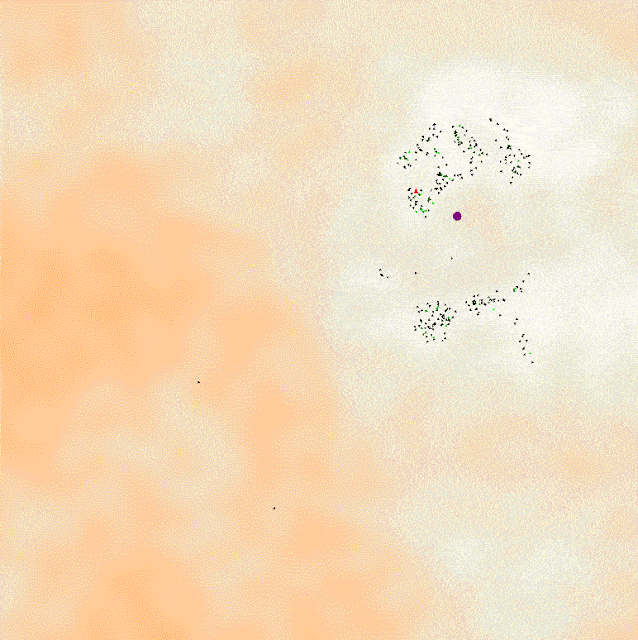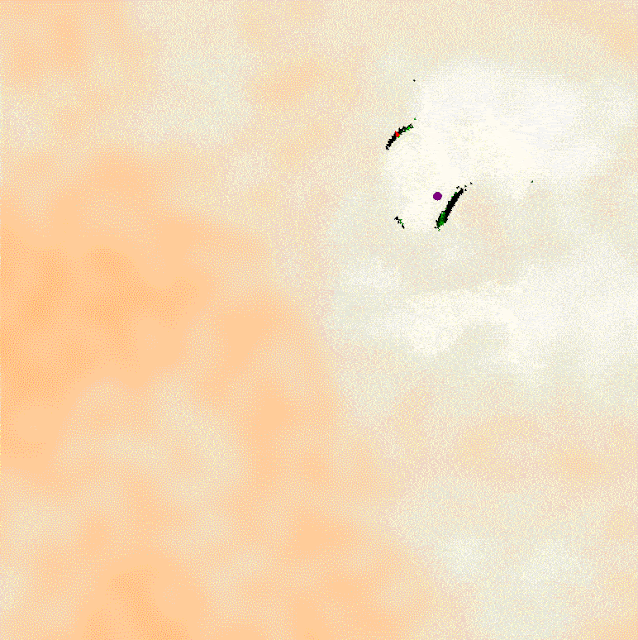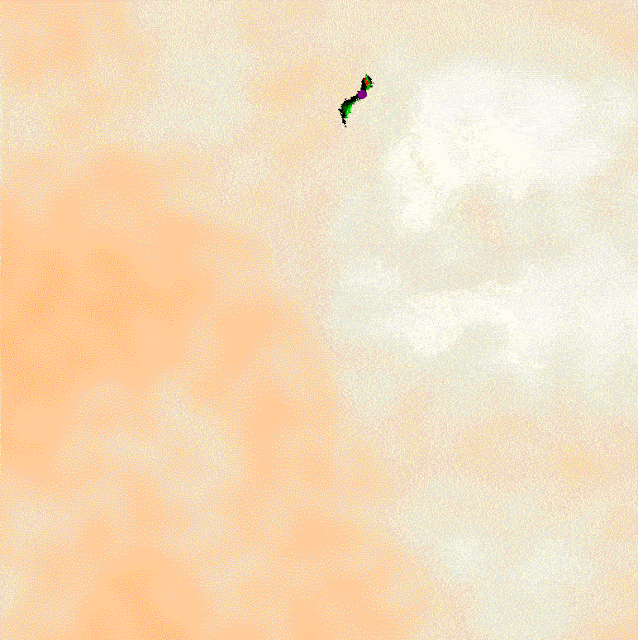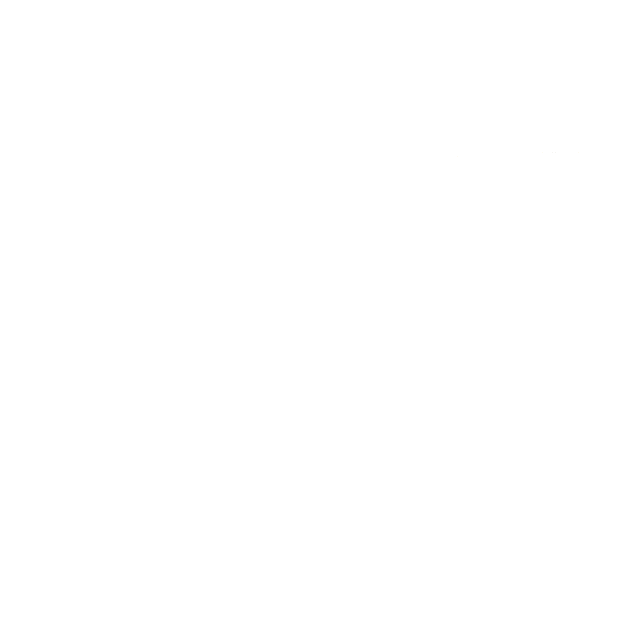
I've implemented a Kalman filter that takes noisy sensor data regarding the x and y positions of the asteroids in this simulation to infer the velocity and acceleration based on the bivariate normal distribution. This data is used to navigate a ship from the bottom to the top of the screen, avoiding all of the asteroids by using their predicted future positions. This is part of the Artificial Intelligence for Robotics course for the CS Master's program at Georgia Tech.
The Kalman filter is ideal for this application because of its ability to handle noisy data by using the Kalman gain to gradually transition from relying on the sensor to the internal model and because of its ability to infer correlated variables such as velocity and acceleration using a transition function that can define the physical constraints of the system. Because this system uses 6 variables it requires the use of linear algebra matrix operations vs the more 1D application of the Kalman filter.
The ship uses the predicted future positions of the asteroids to, at any given timestep, determine if steering left, right, or center, would bring to nearer or father from the squared euclidean distance of the future position of the nearest asteroid.
Below are samples of the ship using the Kalman filter to avoid the asteroids and reach the goal. The code for the asteroid field and rendering was provided by GaTech; the code for the Kalman filter and ship's navigation strategy was written by me.
Monday, September 23, 2019
Machine Learning Decision Tree w Bagging Implementation
This week I've implemented a decision tree algorithm that splits upon correlation creates a regressor based upon an input set of training data. I've also implemented bagging that uses randomized datasets with replacement to smooth out potential overfitting problems over many trees.
Monday, September 9, 2019
Machine Learning Stock Portfolio Optimization in Python
This week in Machine Learning for Trading I've implemented an optimizer using SciPy that takes any number of stock symbols and most effectively allocates one's portfolio among the provided options based upon previous data in a given date range. The metric for evaluating the profitability of a portfolio is based upon the Sharpe Ratio, which adjusts a stock's income against its risk.

Wednesday, August 28, 2019
Machine Learning Water Turret Pest Deterrent

Monday, July 29, 2019
ProGab ESL Simulated Lecturer App
Final Presentation Video (shown above):
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=0qn-9gx6D7k
Final Presentation Slides:
https://docs.google.com/presentation/d/1G4cxJu8j1GPFE8tThRYGPBhdVQyBBw_DrxXB_hP_ftU/edit?usp=sharing
Final Project Files:
https://drive.google.com/open?id=10VWUoTwekPijgbiV8MwLxMCkxK8vWHYp